基础排序
大约 1 分钟
基础排序
冒泡排序
将每次的最大值通过比对,换位置逐步放到最后面
function sort(nums) {
for(let i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--){
for(let j = 1; j <= i; j++){
if(nums[j-1] > nums[j]) [nums[j-1], nums[j]] = [nums[j], nums[j-1]]
}
}
return nums
}
选择排序
function selectSort(arr){
const result = []
let len = arr.length
for(let i = 0; i< len; i++){
const item = getLarge(arr)
// arr = arr.filter(it => item !== it)
const index = arr.findIndex(s => s == item)
// arr.indexOf(item)
arr.splice(index, 1)
result.push(item)
}
return result
}
function getLarge(arr){
let large = arr[0]
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if(large < arr[i]) large = arr[i]
}
return large
}
Array.prototype.findIndex()
findIndex()方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的索引。若没有找到对应元素则返回-1。
插入排序
function insert(arr) {
for(let i = 1; i< arr.length; i++){
for(let j = i-1; j >= 0; j++ ){
// 将需要插入的值,逐个去与排好序的比对
if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]) [arr[j], arr[j+1]] = [arr[j+1], arr[j]]
}
}
}
已经排好序的最后一位和需要插入的那个做比较
快速排序
实现思路
- 基线条件——为空或只包含一个元素,就不需要排序
- 使用分治让其满足基线条件,取一个基准值将数组分为三部分,对两边数组继续治理
举例说明
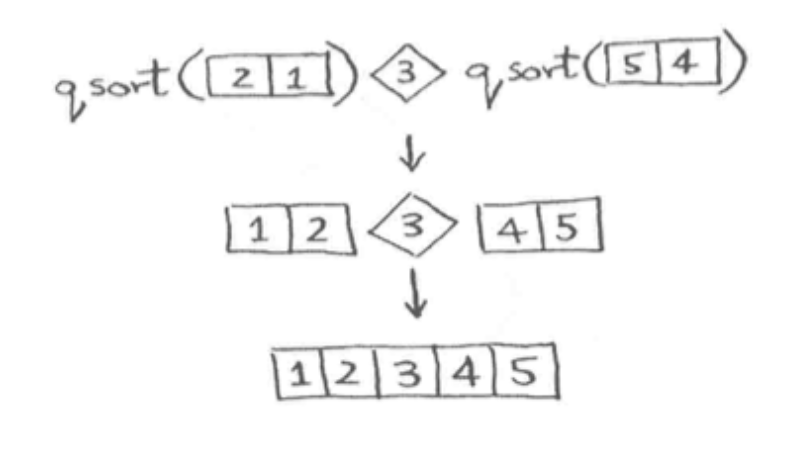
代码实现
function quickSort(arr){
if(arr.length < 2){
return arr
}else{
const pivot = arr[0]
const prv = [];
const next = [];
for(let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i] < pivot){
prv.push(arr[i])
}else{
next.push(arr[i])
}
}
return quickSort(prv).concat(pivot, quickSort(next))
}
}