实现继承
大约 1 分钟
实现继承
原型等于父实例继承
function SuperType() {
this.property = true
}
SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue = function(){
return this.property;
}
function SubType(){
this.subProperty = false
}
// 继承SuperType
SubType.prototype = new SuperType()
SubType.prototype.getSubValue = function(){
return this.subProperty
}
let instance = new SubType()
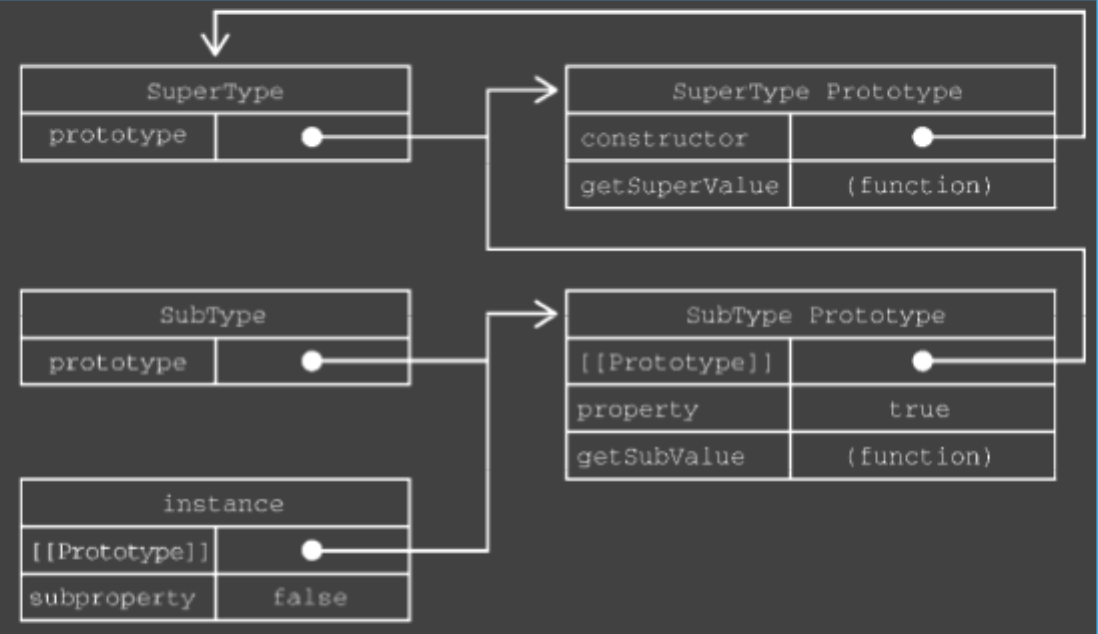
构造函数默认有一个prototype属性,执行原型对象。原型对象默认只会获得 constructor 属性, 执行构造函数。
原型继承问题:
function SuperType() {
this.colors = ['red', 'blue']
}
function SubType(){ }
// 继承SuperType
SubType.prototype = new SuperType()
let instance1 = new SubType()
instance1.colors.push('black')
console.log(instance1.colors) // 'red,blue,black'
let instance2 = new SubType()
console.log(instance1.colors) // 'red,blue,black'
- 包含引用值的问题
- 子类型实例化的时候不能给付类型的构造函数传参
盗用构造函数继承
function SuperType(name) {
this.name = name
this.colors = ['red', 'blue']
}
function SubType(){
// 继承SuperType
SuperType.call(this, 'Nicholas')
this.age = 29
}
let instance1 = new SubType()
instance1.colors.push('black')
console.log(instance1.colors) // 'red,blue,black'
let instance2 = new SubType()
console.log(instance1.colors) // 'red,blue'
盗用构造函数的问题:
- 必须在构造函数中定义方法,函数无法重用
- 无法访问父类原型上的方法
组合继承
function SuperType(name) {
this.name = name
this.colors = ['red', 'blue']
}
SuperType.prototype.sayName = function(){
console.log(this.name)
}
function SubType(name, age){
// 继承属性
SuperType.call(this, name)
this.age = age
}
// 继承方法
SubType.prototype = new SuperType()
SubType.prototype.sayAge = function(){
console.log(this.age)
}
let instance1 = new SubType('Nicholas', 29)
instance1.colors.push('black')
console.log(instance1.colors) // 'red,blue,black'
instance1.sayName() // 'Nicholas'
instance1.sayAge() // 29
let instance2 = new SubType('Greg', 27)
console.log(instance1.colors) // 'red,blue'
instance1.sayName() // 'Nicholas'
instance1.sayAge() // 27
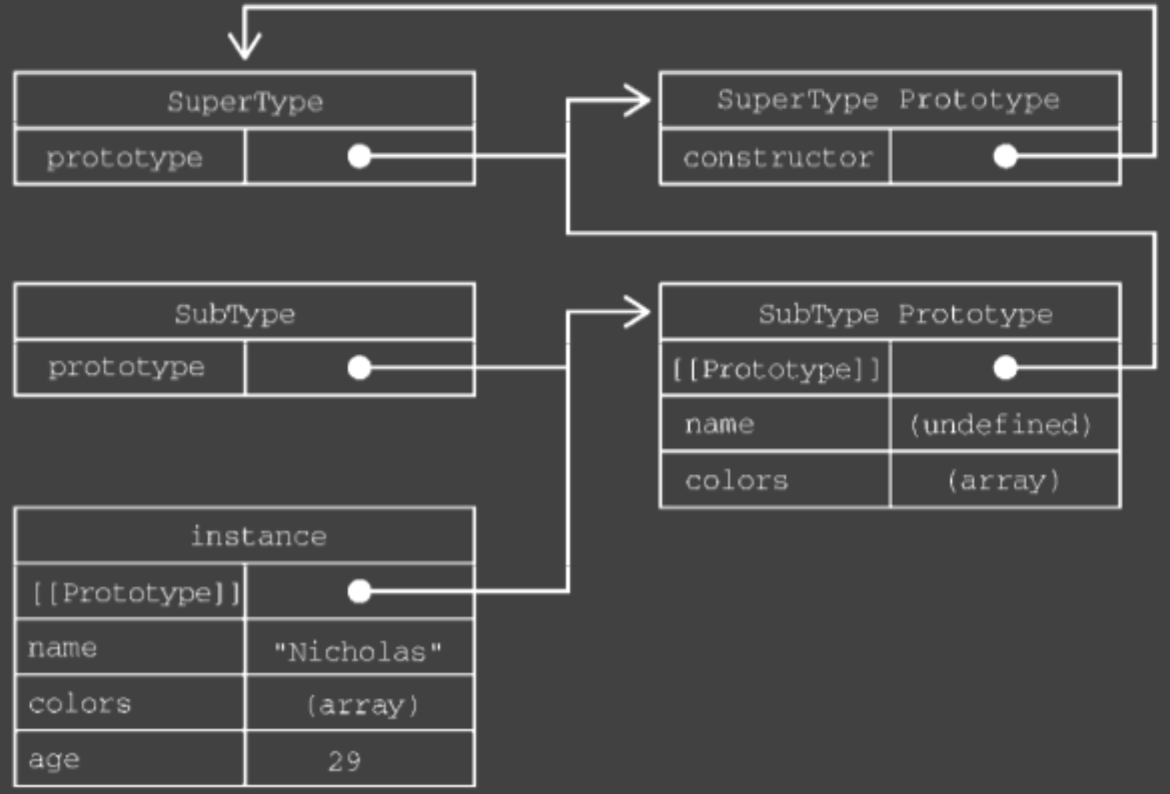
调用 SubType 构造函数时,也会调用 SuperType 构造函数,这一次会在新对象上创建实例属性 name 和 colors。这两个实例属性会遮蔽原型上同名的属性。